The Role of Physical Therapy in Sacroiliitis Treatment
Sacroiliitis is a painful condition that affects the sacroiliac joints, located where the base of your spine (sacrum) connects to your pelvis. This inflammation can cause a range of symptoms, including lower back pain, buttock pain, and sometimes even pain radiating down the leg. While the exact cause can vary, sacroiliitis can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Effective Sacroiliitis Treatment often involves a multi-faceted approach, and physical therapy plays a crucial role. By working closely with a qualified physical therapist, individuals with sacroiliitis can learn effective pain management strategies, develop a personalized exercise program, and improve their overall function and well-being. This comprehensive approach, often complemented by in-home care support, can help individuals achieve their treatment goals and regain control over their lives.
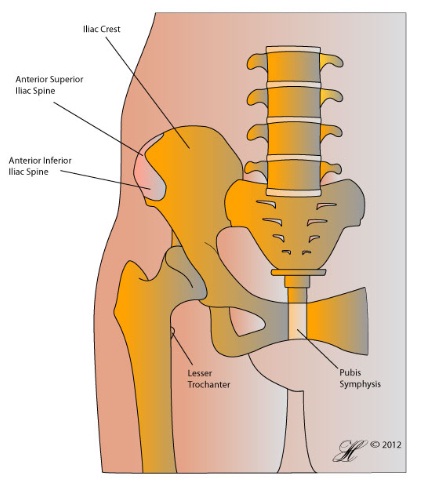
Core Principles of Physical Therapy for Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis Treatment through physical therapy utilizes a multi-faceted approach to address pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function. Key principles include:
Pain Management:
-
- Modalities: Techniques like heat therapy (hot packs, warm baths) can help relax muscles and reduce inflammation. Cold therapy (ice packs) can also be effective in reducing pain and inflammation in acute phases. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) can provide pain relief by interrupting pain signals.
- Manual Therapy: Skilled therapists employ techniques like massage, myofascial release, and joint mobilization to alleviate pain, improve joint mobility, and reduce muscle tension.
Improving Mobility and Flexibility:
-
-
- Stretching is crucial: Regular stretching exercises improve flexibility in the lower back, hips, hamstrings, and surrounding muscles. This helps to reduce muscle tightness that can contribute to pain and stiffness.
- Examples of stretches:
- Hamstring stretches: Touching your toes, hamstring curls
- Piriformis stretches: Figure-four stretch, seated piriformis stretch
- Hip flexor stretches: Lunge stretch, kneeling hip flexor stretch
-
Strengthening Exercises:
-
-
-
-
- Core strengthening: Exercises like pelvic tilts, bridges, and side-lying leg raises are essential to stabilize the pelvis and improve core stability.
- Glute strengthening: Exercises that target the gluteus muscles, such as clamshells and glute bridges, help to support the pelvis and improve hip function.
-
-
-
Postural Correction:
-
- Maintaining proper posture is crucial for reducing stress on the sacroiliac joints.
- Tips:
- Maintain good sitting posture with proper lumbar support.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing.
- Practice proper lifting techniques to avoid strain on the back.
Ergonomic Considerations:
-
- Modifying your workspace and daily activities can significantly reduce stress on the sacroiliac joints.
- Tips:
- Use an ergonomic chair with proper lumbar support.
- Adjust your workstation to ensure proper ergonomics.
- Take frequent breaks to stretch and move around.
In-Home Care Support:
-
- In-home care providers can play a valuable role by assisting with exercises, providing reminders to perform stretches and exercises, and ensuring adherence to the home exercise program. They can also help with activities of daily living, allowing individuals to conserve energy and focus on their recovery.
Specific Exercises and Techniques
This section will delve into some specific exercises and techniques commonly employed by physical therapists within the context of Sacroiliitis Treatment.
Pelvic Tilts:
-
- Technique: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Gently rock your pelvis forward and backward, engaging your abdominal muscles.
- Benefits: This exercise helps strengthen core muscles, improve pelvic alignment, and reduce stress on the sacroiliac joints.
Bridge Exercises:
-
- Technique: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Slowly lift your hips off the ground, squeezing your glutes. Hold for a few seconds and then slowly lower back down.
- Variations:
- Single-leg bridge: Lift one leg off the ground while performing the bridge.
- Bridge with a ball: Place a ball between your knees to increase glute activation.
- Benefits: Bridge exercises strengthen the glute muscles, which play a crucial role in supporting the pelvis and stabilizing the sacroiliac joints.
Side-lying Leg Raises:
-
- Technique: Lie on your side with your knees bent and your top leg resting on the bottom leg. Slowly lift your top leg up towards the ceiling, engaging your hip abductor muscles.
- Benefits: This exercise strengthens the hip abductor muscles, which are important for stabilizing the pelvis and improving hip function.
Stretching Exercises:
-
- Hamstring Stretches:
- Toe touches: Sit or stand and reach for your toes, keeping your knees straight.
- Hamstring curls: Lie on your back and bring one knee towards your chest, keeping the other leg straight.
- Piriformis Stretches:
- Figure-four stretch: Lie on your back and cross one ankle over the opposite knee. Gently pull the knee towards your chest.
- Seated piriformis stretch: Sit on a chair with one leg crossed over the other. Gently lean forward towards the crossed leg.
- Hip Flexor Stretches:
- Lunge stretch: Step forward into a lunge position. Lower your back knee towards the ground.
- Kneeling hip flexor stretch: Kneel on one knee and place the other foot flat on the ground in front of you. Gently lean forward until you feel a stretch in the front of your hip.
- Hamstring Stretches:
Manual Therapy Techniques:
-
- Massage: Massage therapy can help to relax muscles, reduce pain, and improve blood flow.
- Myofascial Release: This technique involves applying gentle pressure to release muscle tension and improve tissue flexibility.
- Joint Mobilization: Skilled therapists may use gentle manual techniques to improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness in the sacroiliac joints.
Home Exercise Programs:
-
- A personalized home exercise program is crucial for long-term success.
- It should include a combination of stretching, strengthening, and core stabilization exercises.
- Consistent adherence to the home exercise program is essential for managing symptoms and improving function.
Patient Education and Self-Management
Patient education and self-management are crucial for successful outcomes in sacroiliitis treatment.
Understanding Sacroiliitis:
-
- Learning about the condition, its causes, and potential triggers can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
- Understanding the importance of consistent exercise and adherence to the treatment plan is essential.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
-
- Excess weight can put additional strain on the sacroiliac joints, exacerbating pain and limiting mobility.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly improve symptoms.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers:
-
- Recognizing activities that aggravate symptoms (e.g., prolonged sitting, heavy lifting) is crucial for managing pain and preventing flare-ups.
- Modifying activities or finding alternative strategies can help individuals minimize discomfort.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider:
-
- Open communication with your physical therapist and other healthcare providers is essential.
- Regularly discuss your progress, any concerns or challenges you may be experiencing, and any changes in your symptoms.
- This ongoing communication allows for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
The Role of In-Home Care Support:
-
- In-home care providers can play a vital role in supporting patient education and self-management.
- They can provide reminders for exercises, assist with medication schedules, and help individuals maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Their support can enhance adherence to the treatment plan and improve overall outcomes.
By actively participating in their care, individuals with sacroiliitis can significantly improve their quality of life and manage their condition effectively.
Conclusion
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of successful Sacroiliitis Treatment, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals living with this condition. By addressing pain, enhancing mobility, and strengthening key muscles, physical therapy empowers individuals to take an active role in their own care.
A comprehensive approach that incorporates a personalized exercise program, pain management techniques, and patient education is crucial for successful outcomes.
The support of in-home care providers can significantly enhance the effectiveness of physical therapy by assisting with exercises, promoting adherence to the treatment plan, and providing valuable support with daily activities.
It is essential to consult with a qualified physical therapist for a thorough evaluation and a personalized Sacroiliitis Treatment plan tailored to individual needs and goals. With consistent effort and a multi-faceted approach, individuals with sacroiliitis can effectively manage their symptoms, improve their function, and regain control over their lives.
Reference Links: