Obesity: A Closer Look
Definition of Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation that presents health risks. It is typically measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese.
Prevalence and Statistics
Obesity has become a global epidemic, affecting over 650 million adults worldwide. In the United States alone, approximately 42% of adults are classified as obese, a significant increase over the past few decades.
Impact on Individuals, Families, and Society
Obesity impacts more than just physical health; it affects mental well-being, economic productivity, and overall quality of life. Families may face emotional and financial strain, while society bears the burden of increased healthcare costs and loss of productivity.
Understanding Obesity
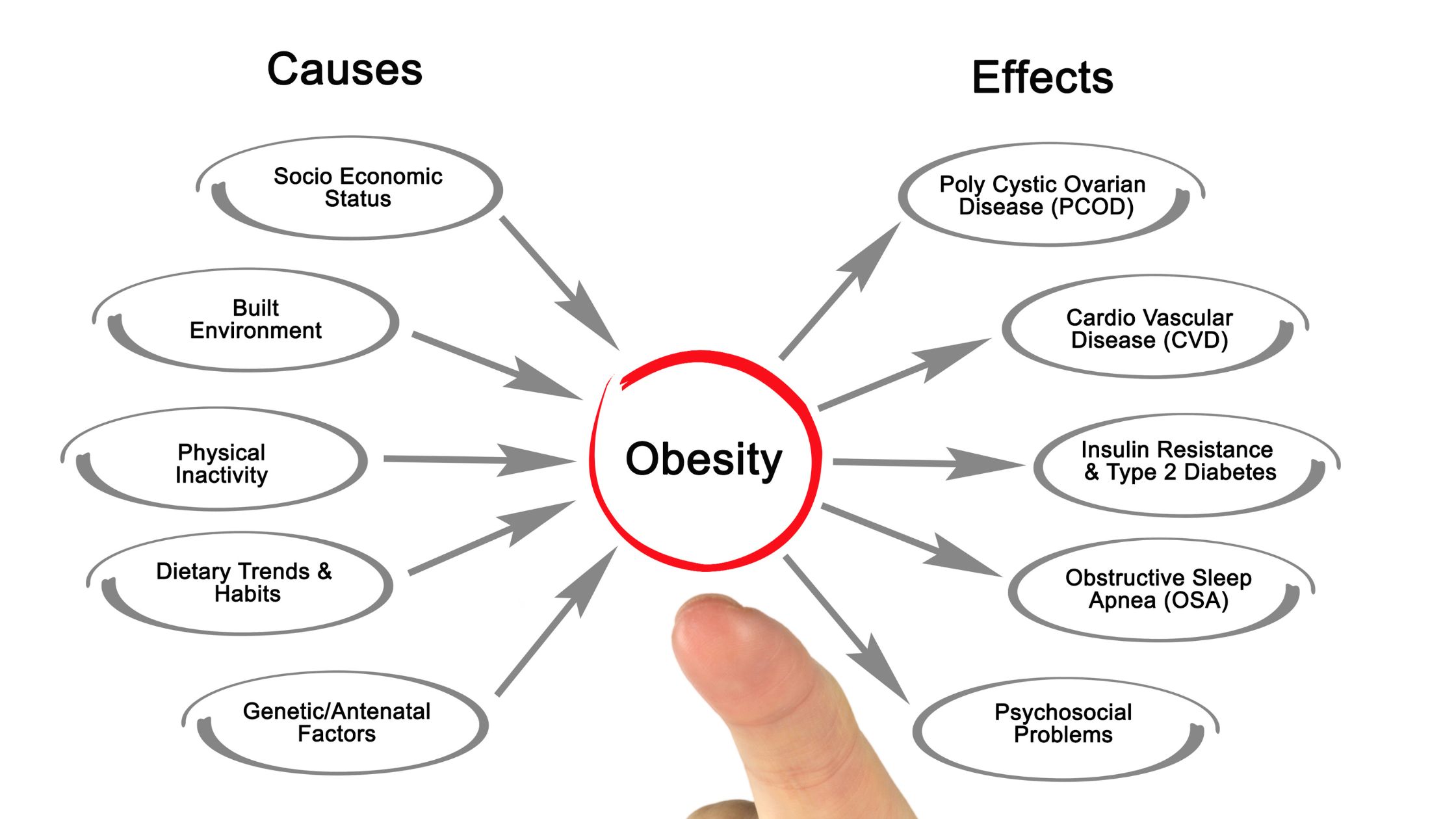 Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk Factors
Obesity is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. Common causes include:
- Poor diet high in calories, fats, and sugars
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Genetic predisposition
- Psychological factors such as stress and emotional eating
Symptoms and Progression
Symptoms of obesity can include:
- Increased body fat, particularly around the abdomen
- Difficulty performing physical activities
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue Obesity often progresses gradually, starting with weight gain that becomes harder to control over time.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosis typically involves calculating BMI and assessing waist circumference. Healthcare providers may also evaluate a patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and physical health to determine the presence of obesity-related complications.
Living with Obesity
Daily Challenges and Coping Mechanisms
Living with obesity can present daily challenges, such as:
- Physical discomfort and mobility issues
- Social stigma and discrimination
- Emotional distress and low self-esteem Effective coping mechanisms include seeking social support, engaging in physical activity, and developing a healthy relationship with food.
Managing Symptoms
Managing obesity involves addressing weight-related health conditions like:
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Joint pain
Emotional and Psychological Support
Support from mental health professionals, support groups, and family can play a crucial role in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of obesity.
Treatment and Management
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are fundamental in managing obesity:
- Diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or strength training.
- Behavior Therapy: Techniques to modify eating habits and address emotional eating.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to assist with weight loss. These can help reduce appetite, increase feelings of fullness, or block fat absorption.
Surgery
For individuals with severe obesity, bariatric surgery (e.g., gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy) can be an effective treatment option. This surgery reduces the stomach’s size, limiting food intake and promoting weight loss.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, and yoga may provide additional support by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Complications of Obesity
Obesity is associated with various health complications, including:
- Heart Disease: Increased risk of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and heart failure.
- Stroke: Higher likelihood of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is a major risk factor for developing insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Sleep Apnea: Excess weight can lead to obstructed airways during sleep.
- Certain Types of Cancer: Increased risk of cancers such as breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer.
Obesity Prevention
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Preventing obesity involves promoting:
- Balanced Diet: Emphasizing nutritious foods and portion control.
- Regular Exercise: Encouraging physical activity from a young age.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through sustainable habits.
Education and Awareness
Public health initiatives aimed at educating people about the risks of obesity and the benefits of a healthy lifestyle are crucial.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing Research Efforts
Current research focuses on understanding the genetic and environmental factors contributing to obesity and developing new treatment methods.
Potential Breakthroughs and Emerging Treatments
Innovative treatments, such as personalized medicine and advanced surgical techniques, hold promise for more effective obesity management.
Advocacy and Awareness Initiatives
Organizations and advocacy groups work tirelessly to raise awareness about obesity and advocate for policy changes that support healthier lifestyles.
Resources and Support
Organizations and Support Groups
Numerous organizations provide resources and support for those affected by obesity:
- American Obesity Association (AOA): Advocacy and support.
- Obesity Action Coalition (OAC): Education and community support.
- Weight Watchers: Programs for weight management and support.
Healthcare Professionals Specializing in Obesity
Specialists such as endocrinologists, dietitians, and bariatric surgeons play a vital role in managing obesity.
Financial Assistance and Insurance Coverage
Understanding insurance coverage for obesity treatments and exploring financial assistance programs can help manage costs.
Special Conditions
Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a growing concern, with long-term implications for physical and mental health. Early intervention is crucial.
Obesity and Mental Health
There is a bidirectional relationship between obesity and mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Obesity and Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic status can influence access to healthy foods, recreational facilities, and healthcare, affecting obesity rates.
Conclusion
Obesity is a complex condition requiring a multifaceted approach to management and prevention. Through lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and emotional support, individuals can improve their health and quality of life. Ongoing research and advocacy efforts continue to advance our understanding and treatment of obesity, offering hope for better outcomes in the future.
Reference Links
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Obesity
CDC Obesity - World Health Organization (WHO) – Obesity and Overweight
WHO Obesity - Mayo Clinic – Obesity
Mayo Clinic Obesity - National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – Health Risks of Overweight and Obesity
NIDDK Obesity - American Heart Association (AHA) – Obesity Information
AHA Obesity - Obesity Action Coalition (OAC) – Understanding Obesity
OAC Obesity

